a.k.a. Adaptive Boosting
- Boosting method (sequential ensemble)
- pay more attention to the training instances that the predecessor predictor under-fitted
- Weights of the misclassified predictions are increased in order to pay more emphasis on these predictions while making the next predictor.
- cannot be parallelized
Algorithm
- each data point instance weight w(i)= 1/m
- m = total number of points
- train 1st predictor
- for predictor j, weighted error rate rj calculated on the training data
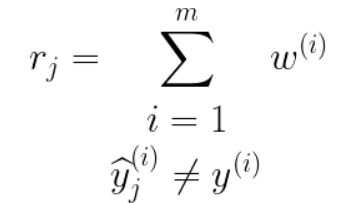
- add up weights of missclassifications
- predictor weight **αj
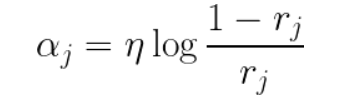
- more accurate the predictor is, the higher its weight
- random guesses ⇒ weight = 0
- update data point instance weights w(i)
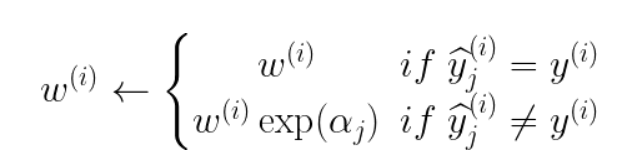
- misclassified instances are weighted more
- normalize all weights
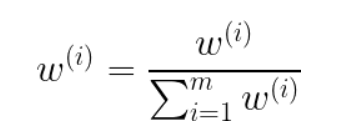
- repeat process on the next predictor (until k predictors) with the weighted instances
Inference mode
- compute the predictions of all the predictors and weighs them using the predictor weight αj
- predicted class → majority weighted vote